Personal data cybersecurity has become increasingly important in recent years with the rise of cyber threats and data breaches. As more people rely on technology to store and share personal information, it is crucial to take the necessary steps to protect that data from falling into the wrong hands. In this article, we will discuss the five best strategies for personal data cybersecurity that everyone should know.
The first strategy is to use strong and unique passwords for all accounts. Passwords should be at least 12 characters long and include a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. It is also important to use a different password for each account to prevent hackers from accessing all accounts if one password is compromised. Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication can add an extra layer of security to accounts, requiring a code or notification in addition to a password to access an account.
Understanding the Threat Landscape
Personal data cybersecurity is a serious concern in today’s digital world. Cyber threats are evolving and becoming more sophisticated, making it essential to understand the threat landscape. This section will cover the types of cyber threats and common attack vectors that individuals may encounter.
| Threat Type | Percentage of Incidents |
|---|---|
| Phishing Attacks | 30% |
| Malware | 25% |
| Social Engineering | 20% |
| Denial of Service | 15% |
| Advanced Threats | 10% |
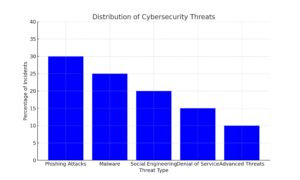
Types of Cyber Threats
There are various types of cyber threats that individuals may encounter. These include:
- Phishing attacks: These attacks involve tricking individuals into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials or credit card details through fraudulent emails or websites.
- Malware: Malware is malicious software that can infect a device and cause harm. This includes viruses, Trojans, and ransomware.
- Social engineering: Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into divulging sensitive information through psychological manipulation.
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks: DoS attacks involve overwhelming a system with traffic to cause it to crash or become unavailable.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs): APTs are sophisticated attacks that involve gaining unauthorized access to a system and remaining undetected for an extended period.
Common Attack Vectors
Attackers can use various methods to gain access to personal sensitive data. Common attack vectors include:
- Emails: Phishing attacks often occur through email, with attackers sending fraudulent emails that appear to be from a legitimate source.
- Social media: Social media platforms can be used to gather personal information and launch social engineering attacks.
- Software vulnerabilities: Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in software to gain unauthorized access to a system.
- Unsecured networks: Public Wi-Fi networks are often unsecured, making them vulnerable to attacks.
- USB drives: USB drives can be used to spread malware and gain unauthorized access to a system.
Understanding the threat landscape is the first step in protecting personal data from cyber threats. By being aware of the types of cyber threats and common attack vectors, individuals can take steps to mitigate the risks and safeguard their personal data.
Strengthening Passwords and Authentication

In today’s digital world, passwords are the first line of defense against cyber threats. Therefore, it is essential to create strong passwords and use multi-factor authentication to secure personal data.
Creating Strong Passwords
Creating a strong password is crucial to ensuring the safety and security of personal and professional information. According to CISA.gov, a strong password should have the following characteristics:
- At least 12 characters long
- A combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters
- Not contain any personal information such as name, date of birth, or address
It is also recommended to use a password manager to generate and store strong passwords securely. Password managers such as Dashlane utilize AES-256 encryption, which is widely accepted as the strongest encryption type available, to protect passwords before they are stored in secure cloud locations. While encryption isn’t a substitute for a strong, unique password, it does help protect passwords from cyber criminals.
Using Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is an additional layer of security that requires users to provide two forms of identification to access control over their accounts. This can be a password and a code sent to a user’s phone or email, a biometric scan, or a physical token.
Enabling 2FA adds an extra layer of security to online accounts, making it more difficult for hackers to access personal data. Many online services, such as Google, Facebook, and Twitter, offer 2FA as an option.
In conclusion, creating strong passwords and using two-factor authentication are essential strategies for personal cybersecurity. By following these best practices, users can protect their personal and professional information from cyber threats.
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Regular software updates and patch management are essential for personal data cybersecurity. When vendors become aware of vulnerabilities in their products, they often issue patches to fix those vulnerabilities. Applying relevant patches to your computer as soon as possible can protect your system from security breaches.
Effective patch management involves a systematic approach to identifying, testing, and applying patches to your systems and applications. Organizations should develop a comprehensive patch management policy outlining procedures, responsibilities, and timelines.
Scheduling regular patch updates ensures that software and systems are always up-to-date and secure. Organizations should schedule these updates for a time that is convenient for their operations. They should also educate employees on the importance of updating software and systems in a timely manner. Compliance with industry regulations and data protection standards is also a benefit of keeping software up to date.
Below are some best practices for patch management:
- Establishing a patch management policy outlining procedures, responsibilities, and timelines
- Testing patches in a non-production environment before applying them to production systems
- Prioritizing patches based on severity and potential impact on the organization
- Ensuring that all systems and applications are covered by the patch management policy
- Keeping track of each security patch as it is released
In summary, regular software updates and patch management are crucial for personal data cybersecurity. Organizations should develop a comprehensive patch management policy, schedule regular patch updates, and educate employees on the importance of updating software and systems in a timely manner.
Implementing Advanced Security Measures
When it comes to personal data cybersecurity, implementing advanced security measures is crucial. Here are two important measures that can help protect your personal data:
Encryption and Secure Connections
Encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. It is one of the most effective ways to protect personal data. By encrypting personal data, even if a hacker gains access to it, they will not be able to read it without the encryption key.
Secure connections are also important for personal data cybersecurity and physical security. When connecting to the Internet, it is important to ensure that the connection is secure. This can be done by using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or by ensuring that the website being accessed has a valid SSL certificate.
Antivirus and Anti-Malware Solutions
Antivirus and anti-malware solutions are essential for protecting personal data from malicious software. These solutions work by scanning the computer for viruses and malware and removing them. It is important to keep these solutions up-to-date to ensure that they are effective against the latest threats.
In addition to antivirus and anti-malware solutions, it is also important to be cautious when downloading and installing software. It is recommended that you only download software from reputable sources and read reviews before downloading.
By implementing advanced security measures such as encryption, secure connections, antivirus, and anti-malware solutions, individuals can protect their personal data from cyber threats.








