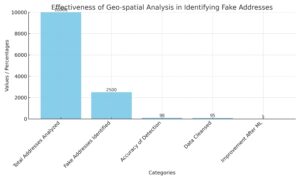
Geo-spatial data is crucial for understanding location-based trends but is vulnerable to manipulation like the creation of fake addresses. This can mislead individuals or organizations. To tackle fake address issues, data scientists use various methods, including statistical analysis and machine learning, to detect and prevent manipulation.
Tips for Geo-Spatial Manipulation of Fake Addresses
Geo-spatial manipulation of fake addresses is a critical process for businesses that rely on location data to make informed decisions. Here are some tips to help businesses manipulate fake addresses effectively:
Tip 1: Identifying Fake Addresses

The first step in geo-spatial manipulation of fake addresses is to identify fake addresses. Using geo-spatial analysis, businesses can detect fake addresses by analyzing the spatial patterns of the data. There are several tools and techniques for detection, including clustering algorithms and anomaly detection methods.
Tip 2: Data Cleansing and Validation

Once fake addresses are identified, the next step is to cleanse and validate the data. Techniques for cleaning geo-spatial data include removing duplicates, correcting spelling errors, and standardizing formats. Validating addresses with geo-spatial tools can help ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Tip 3: Leveraging Machine Learning

Machine learning can be used to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of geo-spatial manipulation. By building models to detect anomalies, businesses can improve their ability to identify and manipulate fake addresses. Machine learning can also be used to automate data cleansing and validation processes.
Tip 4: Integrating Geo-Spatial Data with Other Datasets

Integrating geo-spatial data with other datasets can enhance data accuracy and provide businesses with a more comprehensive view of their operations. Techniques for enhancing data accuracy include geocoding, which involves assigning latitude and longitude coordinates to addresses, and spatial join, which involves combining data from different sources based on their spatial relationships. Case studies of successful integration can provide valuable insights into the benefits of integrating geo-spatial data with other datasets.
Tip 5: Continuous Monitoring and Updating

Regular data updates are essential for maintaining data accuracy and ensuring that businesses have access to the most up-to-date information. Tools for continuous geo-spatial data monitoring can help businesses stay informed about changes in their operations and make informed decisions based on the latest information.