The rise of the internet has led to a significant increase in the amount of data that is generated and transferred across the globe. As a result, governments and private organizations have developed sophisticated surveillance systems to monitor online activities. This section explores the historical context and evolution of internet surveillance.
From the Early Internet to the Digital Age
The early internet was a decentralized network where users could connect without central oversight. As it gained popularity, it also became a target for surveillance by governments and corporations. In the 1990s, the US government introduced the Carnivore program to monitor online communications for law enforcement purposes.
After the events of September 11, 2001, surveillance intensified globally. New laws and technologies were implemented to watch over online activities. Notably, the USA PATRIOT Act granted the US government extensive powers to monitor internet traffic, even without a warrant.
Technological Advances and Surveillance Capabilities
Technological advances have greatly enhanced surveillance capabilities for governments and corporations. Social media platforms provide access to vast personal data, enabling authorities to track and monitor individuals. Big data analytics allow for the real-time analysis of huge data sets, revealing patterns and trends that traditional methods might miss. Additionally, facial recognition technology has equipped law enforcement with the tools to identify individuals instantly in public spaces.
Legal Frameworks and Privacy Rights

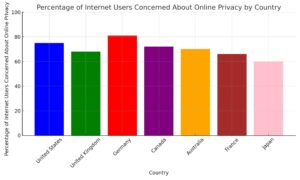
The legal frameworks surrounding online privacy rights vary widely across different jurisdictions, making it difficult to establish a universal standard for protecting personal information on the internet. This section will examine the jurisdictional variances in privacy laws and the role of international human rights in shaping privacy legislation.
Jurisdictional Variances in Privacy Laws
The Role of International Human Rights
Impact of Surveillance on Individual Autonomy
The right to privacy is considered a fundamental human right and is enshrined in international law. However, with the rise of digital surveillance, individual autonomy is being threatened. The impact of surveillance on individual autonomy can be analyzed from different angles, including the psychological effects of being monitored and the consequences for freedom of expression.
Psychological Effects of Being Monitored
The mere awareness of being monitored can have a significant impact on an individual’s behavior. Research has shown that individuals who are aware of being monitored tend to self-censor and modify their behavior to conform to societal norms. This is known as the “chilling effect” and can lead to a loss of individual autonomy.
Moreover, surveillance can create a feeling of distrust between individuals and the government or other entities conducting the surveillance. This can lead to a breakdown in trust, which is essential for a functioning democracy. When individuals feel that they are being watched, they may also feel that their privacy is being invaded, which can lead to a sense of powerlessness and loss of control over their lives.
Consequences for Freedom of Expression
Surveillance can also have a significant impact on freedom of expression. When individuals are aware that their online activities are being monitored, they may self-censor and avoid expressing their true opinions on controversial issues. This can lead to a chilling effect on free speech, which is essential for a functioning democracy.
Moreover, surveillance can lead to censorship and the suppression of dissenting voices. Governments or other entities conducting surveillance may use their power to silence those who disagree with them. This can lead to a loss of individual autonomy and a breakdown in trust between individuals and the government.
The Future of Online Privacy and Surveillance
The proliferation of emerging technologies such as facial recognition, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has raised concerns about the future of online privacy and surveillance. As the world becomes more connected, the amount of data being generated and collected is increasing exponentially. This has led to the rise of surveillance capitalism, a business model that relies on the collection and analysis of user data to generate revenue.