With the rise of digital healthcare and telemedicine, the protection of online health data privacy has become more important than ever. Online health data includes personal information such as medical histories, test results, and prescription details. This type of information is highly sensitive and can be used for malicious purposes if it falls into the wrong hands. Therefore, it is crucial to take steps to protect online health data privacy.

To help individuals protect their online health data privacy, experts have compiled a list of top 10 tips. These tips include using unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, avoiding public Wi-Fi networks, and using a virtual private network (VPN) when accessing health data online. It is also important to keep apps and software up to date and to be cautious of phishing scams and suspicious emails. By following these tips, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of their online health data being compromised. In addition to these tips, it is important to be aware of the privacy policies of healthcare providers and to only share personal health information when necessary. It is also recommended to regularly review online health data for accuracy and to report any suspicious activity to healthcare providers or law enforcement. By taking a proactive approach to online health data privacy, individuals can ensure that their sensitive information remains secure.
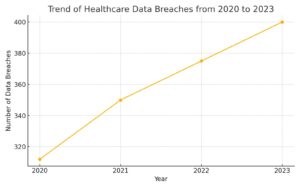
| Year |
Number of Healthcare Data Breaches |
Records Affected (Millions) |
Percentage of Hospitals Affected |
| 2020 |
312 |
5.2 |
45% |
| 2021 |
350 |
6.8 |
50% |
| 2022 |
375 |
7.5 |
55% |
| 2023 |
400 |
9.0 |
60% |
10 Essential Strategies to Secure Your Online Health Information

Protecting online health data privacy is essential in today’s digital age. Cybercriminals are always looking for ways to steal personal information, including your health data.
Here are ten essential strategies to secure your online health information:
1. Use Strong Passwords:
Using strong passwords is one of the most fundamental yet effective ways to enhance your online health data cybersecurity. A strong password should be long—ideally more than 12 characters—and include a mix of letters (both uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and symbols. This complexity makes it much harder for cybercriminals to guess or crack your password using brute force techniques.
Additionally, it’s crucial to avoid using the same password across multiple accounts. If a hacker gains access to one of your passwords and you reuse it elsewhere, they can easily access other important accounts, compromising your overall security. To manage the challenge of remembering different passwords for various accounts, consider using a password manager.
A password manager is a tool that generates, retrieves, and keeps track of complex passwords for you, storing them in a secure, encrypted database. You only need to remember one strong master password to access all your other passwords. This not only bolsters your security but also makes it more convenient to manage your credentials across different services and platforms.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication:
Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds a critical layer of security to control access to your data, requiring more than just a password for access. When 2FA is active, after entering your password, you must also verify your identity using a second method. This can be a code from a trusted authentication app like Google Authenticator or Authy, which generates time-sensitive codes on your phone. Alternatively, you might use a physical security key, a small device that you plug into your computer or link via Bluetooth, providing robust protection by ensuring that only someone with physical possession of the key can access your account.
3. Keep Software Updated:
Keeping your software updated is crucial for securing your online data. Software updates often include patches for security vulnerabilities discovered since the last update. By regularly updating your operating system, antivirus software, and other applications and ensuring you have a secure backup system, you fortify these potential entry points against hackers and protect your data more effectively in case of an attack. This not only protects your health data but also secures other sensitive information on your device.
Neglecting software updates can leave you exposed to known threats and cyber attacks. Setting your devices to update automatically can help maintain your security without having to manually check for updates, ensuring you always have the latest protections in place.
4. Use Secure Networks:
Using secure networks is essential when handling sensitive information such as online health data. Public Wi-Fi networks, often found in places like cafes, airports, and hotels, are not secure. They provide an easy way for cybercriminals to intercept your internet traffic and steal personal data. To avoid this risk, refrain from performing personal tasks or accessing sensitive information on these networks.
Instead, use a virtual private network (VPN). A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it difficult for anyone on the same network to monitor or intercept your activities. This encryption helps protect your data as it travels through the internet, ensuring that your online activities, from accessing health records to making transactions, are secure.
5. Be Wary of Links and Attachments:
Being cautious with links and attachments is critical to maintaining your online safety, especially in the context of health data privacy. Cybercriminals often use phishing emails, which appear to come from legitimate sources, to trick you into clicking on malicious links or opening harmful attachments. These can lead to malware infections or direct you to fake websites designed to steal your personal and financial information.
To protect yourself, always verify the sender’s identity before clicking on any links or downloading attachments, even if they appear to come from a known contact or reputable organization. Look for signs of authenticity, such as correct spelling and grammar, and verify the email address or link destination by hovering over them. If in doubt, contact the sender directly using a known email or phone number to confirm the message’s legitimacy before taking any action.
6. Limit Data Sharing:
Limiting data sharing is a key strategy in protecting your online health data privacy. Be selective about what personal information you share and with whom, especially when it involves sensitive health details. Third-party apps and services often request access to your data, but it’s essential to assess whether sharing this information is necessary for the service they provide.
Before agreeing to share your data, thoroughly read the privacy policies and terms of service. These documents outline how your information will be used, stored, and protected. Look for assurances of data encryption and regulations compliance, like HIPAA in the U.S., which provide layers of security. If a company’s privacy policy is vague or lacks clear protections, consider it a red flag and weigh the risks of sharing your data with them.
7. Read Privacy Policies:
Reading privacy policies is crucial in managing the security and privacy of your health information. These policies detail how your data is collected, stored, and shared by various entities, including healthcare providers, insurers, and third-party apps. By understanding these details, you can make informed decisions about who you trust with your sensitive information.
It’s important to look for specific information in these policies, such as the types of data collected, the purposes for data collection, how long the data is retained, and the security measures in place to protect your information. Also, check how these entities handle data sharing with third parties and under what circumstances they might disclose your information. If a policy does not clearly address these points or suggests lax security practices, it might be wise to reconsider providing your personal health data to such entities.
8. Use Reputable Apps and Services:
Choosing reputable apps and services is vital for safeguarding your online health data and enhancing data protection measures. Opt for those that have positive reviews and are known for their strong privacy practices. It’s important to select apps and services that are transparent about how they handle data collection, usage, and protection.
Look for apps and services that explicitly state their security measures, such as data encryption and compliance with relevant privacy laws (like HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe). Also, check whether these apps have undergone independent security audits. Reading user reviews can provide insights into the reliability of the app and any potential privacy issues experienced by others. This approach ensures you use only those applications that prioritize and actively protect your personal health information.
9. Log Out After Use:
Always logging out from apps and websites after use is a simple yet effective practice for maintaining your online security, especially when handling sensitive health data. Leaving your accounts open on shared devices or public computers can leave you vulnerable to unauthorized access. Even on personal devices, logging out can prevent accidental data exposure or misuse if your device is lost or stolen.
By taking the extra step of logging out, you ensure that your information remains secure and prevent potential intruders from gaining access to your private data. This habit is particularly important in public or workplace environments where multiple users might access the same device. Making a routine of logging out can significantly enhance your overall data security posture.
10. Monitor Account Activity:
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential steps to ensure the security of personal health information online?
To ensure the security of personal health information online, individuals and organizations should take several essential steps. First and foremost, they should use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication wherever possible. Secondly, they should avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for accessing sensitive information. Thirdly, they should keep their software and operating systems up-to-date with the latest security patches. Finally, they should use encryption to protect data and ensure sensitive data is secure both in transit and at rest.
How can healthcare organizations strengthen their defenses against cyber attacks?
Healthcare organizations can strengthen their defenses against cyber attacks by implementing a comprehensive information security program. This program should include regular risk assessments, employee training, and incident response planning. Additionally, organizations should use security tools such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and antivirus software to protect their networks and endpoints.
What best practices should be followed to protect patient health information in the workplace?
To protect patient health information in the workplace, employees should follow best practices such as limiting access to sensitive data on a need-to-know basis, logging off when leaving their workstations, and reporting any suspicious activity to their supervisor. Additionally, organizations should implement technical safeguards such as access controls, audit logs, and data encryption to protect sensitive information.
In what ways can individuals maintain the privacy of their health data when using telehealth services?
To maintain the privacy of their health data when using telehealth services, individuals should ensure that they are using a secure and encrypted connection to communicate with their healthcare provider. They should also verify that the telehealth platform they are using is compliant with relevant privacy and security regulations such as HIPAA. Finally, individuals should be cautious when sharing sensitive information over telehealth platforms and should only do so when necessary.
What measures can be taken to safeguard sensitive health information from unauthorized access?
To safeguard sensitive health information from unauthorized access, individuals and organizations should implement access controls such as passwords, biometric authentication, and two-factor authentication. Additionally, they should use encryption to protect sensitive data in transit and at rest. Finally, they should monitor their systems and networks for suspicious activity and take prompt action to address any security incidents.
How does the importance of data security in healthcare translate into actionable strategies for individuals and organizations?
The importance of data security in healthcare translates into actionable strategies for individuals and organizations by emphasizing the need for a comprehensive and proactive approach to information security. This approach should include regular risk assessments, employee training, and incident response planning. Additionally, organizations should implement technical safeguards such as access controls, audit logs, and data encryption to protect sensitive information. Finally, individuals should be vigilant when sharing sensitive information and should take steps to protect their privacy and security online.













