As our lives become increasingly digital, the issue of privacy in the digital age has become a topic of great importance. Online privacy refers to the right of individuals to determine what information they share about themselves online and how that information is used. Ethics, on the other hand, refers to the moral principles that govern behavior, including what is considered right and wrong.
Exploring the ethical implications of online privacy is essential for understanding the impact of our digital lives on our personal and professional lives. The misuse of personal data by companies or malicious actors is one of the key ethical challenges with significant ethical implications for online data privacy and security. As such, it is essential to establish robust ethical guidelines for data protection to safeguard individuals’ privacy. The emotional consequences of online to offline privacy spillovers are also important to consider. Few researchers have explored the link between privacy and emotions, but the scant literature on this topic suggests that privacy concerns correlate negatively with happiness and positively with anxiety.
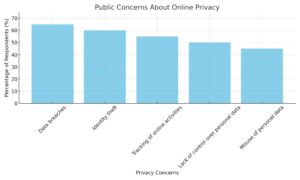
| Concern | Percentage of Respondents |
|---|---|
| Data breaches | 65% |
| Identity theft | 60% |
| Tracking of online activities | 55% |
| Lack of control over personal data | 50% |
| Misuse of personal data | 45% |
The Ethical Landscape of Online Privacy

As the world becomes increasingly digitized, the importance of online privacy ethics has become more apparent. The collection, storage, and use of personal data raise ethical concerns that must be addressed to protect privacy rights and human dignity. This section explores some of the ethical issues surrounding online privacy, including privacy rights, consent and autonomy in data collection, and regulatory frameworks and legislation.
Privacy Rights and Human Dignity
Privacy is a fundamental human right that is enshrined in international law. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights recognizes the right to privacy as a basic human right, stating that “no one shall be subjected to arbitrary interference with his privacy, family, home or correspondence.” The right to privacy is also recognized in the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, the European Convention on Human Rights, and other international treaties and agreements.
Privacy rights are closely linked to human dignity, as the protection of personal information is essential to maintaining autonomy and control over one’s life. The unauthorized collection, use, and disclosure of personal data can have serious consequences, including identity theft, financial fraud, and reputational harm.
Consent and Autonomy in Data Collection
Informed consent is a key ethical principle in the collection and use of personal data, particularly critical for maintaining privacy in the digital age. Individuals have the right to know what data is being collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it. They also have the right to refuse to provide their data or to withdraw their consent at any time.
The principle of autonomy is also important in data collection, as individuals should have the right to control their personal information. This includes the right to access, correct, and delete their data and to know who has access to it.
Regulatory Frameworks and Legislation
Numerous laws and regulations have been enacted to protect online privacy and address the ethical implications related to data collection and use. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive privacy law that applies to all companies that process the personal data of EU citizens. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a state-level law that gives California residents the right to know what data is being collected about them and to opt out of the sale of their data.
The Privacy Act of 1974 is a federal law that regulates the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information by federal agencies. Other laws and regulations that address online privacy include the Electronic Communications Privacy Act, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA).
In conclusion, the ethical landscape of online privacy is complex and multifaceted. Privacy rights, informed consent, and regulatory frameworks are all important considerations in the collection and use of personal data. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential that ethical principles and legal frameworks keep pace to protect privacy and human dignity.
Corporate Responsibility and Data Ethics

In the digital age, companies are collecting and processing vast amounts of personal data. As such, it is essential for companies to establish robust ethical guidelines for data protection to safeguard individuals’ privacy. This section explores the role of corporate responsibility in data ethics, with a focus on data protection and security measures, transparency and accountability in big tech, and the challenges of compliance and enforcement.
Data Protection and Security Measures
Data privacy and data security are critical components of online privacy ethics. Companies have a responsibility to ensure that personal data is collected, processed, and stored securely. This includes implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure, ensuring robust privacy and security.
To achieve this, companies must invest in cybersecurity measures and ensure that they comply with relevant data protection laws and regulations. For example, GDPR requires companies to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure a level of security appropriate to the risk.
Transparency and Accountability in Big Tech
Big tech companies such as Google, Facebook, and Amazon have access to vast amounts of personal data. As such, they have a responsibility to be transparent about how they collect, use, and share this data. This includes providing users with clear and concise privacy policies, allowing users to control their data, and being accountable for any data breaches or misuse of personal data.
Big tech companies are increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI) to process and analyze personal data. As such, it is essential for companies to be transparent about how AI is used and to ensure that it is used ethically and responsibly.
Challenges of Compliance and Enforcement
Compliance with data protection laws and regulations can be challenging for companies, particularly those operating in multiple jurisdictions. Companies must comply with a range of laws, including GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, and ensure that they keep up to date with any changes to these laws.
Enforcement of data protection laws and regulations can also be challenging. Companies that violate data protection laws may face fines, legal action, or damage to their reputation. However, enforcement action can be slow, and fines may not be sufficient to deter companies from engaging in unethical data practices.
In conclusion, corporate responsibility plays a crucial role in data ethics. Companies must ensure that they protect personal data, maintain privacy and security, are transparent about how they use personal data and comply with relevant data protection laws and regulations. However, compliance and enforcement remain significant challenges, and companies must continue to invest in data protection and security measures to safeguard individuals’ privacy.
The Individual’s Role in Online Privacy
The internet has become an integral part of modern life, and with it comes the issue of online privacy. As such, it is essential for individuals to understand their role in protecting their privacy online. This section discusses the individual’s role in online privacy, including understanding and exercising privacy rights and the impact of user behavior on privacy.
Understanding and Exercising Privacy Rights
Individuals have the right to privacy, both offline and online. However, many people are not aware of their privacy rights, or they do not know how to exercise them. It is important for individuals to understand their privacy rights and how to exercise them. For example, individuals have the right to know what personal data is collected and how it is used. They also have the right to control their data and to give or withhold consent for its use.
Individuals should be aware of the regulations and laws that protect their privacy to exercise their rights. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union gives individuals the right to access, correct, and delete their personal data. In the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) gives individuals the right to know what personal data is collected and to opt out of its sale.
The Impact of User Behavior on Privacy
Individual behavior has a significant impact on online privacy. For example, individuals who use weak passwords or reuse them across multiple sites put their personal data at risk. Similarly, individuals who do not read privacy policies or terms of service agreements may unknowingly give away their personal data.
Individuals can take steps to protect their online privacy. For example, they can use strong passwords and two-factor authentication to secure their accounts. They can also use browser extensions that block cookies or prevent tracking. Additionally, individuals can opt out of data collection by adjusting their privacy settings on social media platforms and other websites.
In conclusion, individuals play a crucial role in protecting their online privacy. By understanding and exercising their privacy rights and taking steps to protect their personal data, individuals can maintain control and autonomy over their personal information.
Emerging Technologies and Future Challenges
As technology continues to evolve, so do the ethical challenges surrounding online privacy. The intersection of AI, IoT, and privacy is a particularly pressing concern in the digital age. With the rise of 5G networks and the increasing amount of data being collected, it is important to consider the potential consequences of these technologies.
The Intersection of AI, IoT, and Privacy
Artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) are two technologies that are rapidly changing the way we live and work. However, these technologies also pose significant risks to our privacy. AI algorithms can be biased, leading to discrimination and privacy violations. IoT devices can collect vast amounts of data, which can be used to track individuals and compromise their privacy.
Encryption is one way to protect privacy, but it can also be a double-edged sword. While encryption can help keep data secure, it can also be used to hide illegal activities. Facial recognition is another technology that raises ethical concerns. While it can be used to identify criminals, it can also be used to track innocent individuals.
Anticipating Ethical Dilemmas in Digital Evolution
As technology continues to evolve, it is important to anticipate potential ethical dilemmas. Digital ethics is a field that seeks to address these challenges by creating guidelines for the responsible use of technology. However, it is important to note that these guidelines are only effective if they are followed.
One potential challenge is the use of AI in decision-making. As AI becomes more advanced, there is a risk that it will be used to make decisions that have a significant impact on people’s lives, such as hiring decisions or medical diagnoses. It is important to ensure that these decisions are fair and unbiased.
Another challenge is the use of data for targeted advertising. While targeted advertising can be effective, it can also be invasive. It is important to ensure that individuals have control over their data and how it is used.
In conclusion, emerging technologies present both opportunities and challenges for online privacy ethics. It is important to anticipate potential ethical dilemmas and create guidelines for responsible technology use. By doing so, we can ensure that technology is used in a way that benefits society as a whole.
Video Guide