Geolocation data privacy laws are becoming increasingly essential in today’s digital age. With the widespread use of mobile devices, location-based services, and the Internet of Things (IoT), geolocation data is being collected, processed, and shared more than ever before. This has raised concerns about the privacy and security of individuals’ personal information, as well as the potential for misuse or abuse of this data.

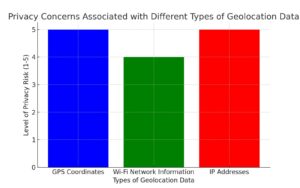
Geolocation data is a type of personal information that can reveal a person’s whereabouts, movements, and activities. It includes information such as GPS coordinates, Wi-Fi network information, and IP addresses. This data is often collected by mobile apps, websites, and other digital services, and used for a variety of purposes, such as targeted advertising, location-based services, and analytics. However, it can also be used for more nefarious purposes, such as stalking, identity theft, and surveillance.
As a result, many countries and jurisdictions around the world have implemented geolocation data privacy laws to protect individuals’ rights. These laws typically require companies to obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting their geolocation data, provide clear and concise privacy policies, and implement appropriate security measures to protect this data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
| Type of Geolocation Data | Common Uses | Privacy Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| GPS Coordinates | Navigation, Fitness tracking | Tracking movements, Location-based targeting |
| Wi-Fi Network Information | Location services, Analytics | Unauthorized access, Data interception |
| IP Addresses | Targeted advertising, Content customization | Identity theft, Location tracking |
Understanding Geolocation Data

Defining Geolocation Data and Privacy
Geolocation data refers to information that identifies the geographic location of an object or person. It can be obtained from various sources, including GPS, triangulation, WiFi capture, and Bluetooth pinging. Geolocation data can be used for a variety of purposes, including tracking the location of mobile devices, providing location-based services, and analyzing consumer behavior.
Privacy concerns surrounding geolocation data arise from the fact that it can reveal sensitive information about an individual’s movements and activities. As a result, many countries have implemented laws and regulations to protect the privacy of individuals’ geolocation data.
The Role of Mobile Devices in Data Collection
Mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets have become ubiquitous in modern society. These devices are equipped with GPS and other sensors that can collect geolocation data. In addition, many applications installed on these devices also collect geolocation data to provide location-based services.
The collection of geolocation data by mobile devices has raised concerns about privacy. While many applications request permission to access a user’s location data, users may not always be aware of the extent to which their data is being collected and used. As a result, many countries have implemented laws and regulations to ensure that individuals have control over their geolocation data and are aware of how it is being used.
The Importance of Geolocation Data Privacy Laws

Geolocation data privacy laws are essential as they protect sensitive personal information that can be used to identify a person’s location. With the increasing use of location-based services and mobile applications, the collection of geolocation data has become a major concern for privacy advocates.
Protecting Sensitive Personal Information
Sensitive personal information such as a person’s location can be used to track their movements, monitor their behavior, and even identify their daily routines.
This information can be used by companies to target advertisements, by law enforcement to track suspects, or by hackers to steal personal information. Geolocation data privacy laws help to protect this sensitive information by regulating the collection, use, and storage of location data.
Regulations and Consumer Rights
Geolocation data privacy laws provide regulations and consumer rights that protect individuals from the misuse of their personal information. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) are examples of regulations that require companies to obtain explicit consent from users before collecting and using their geolocation data. Additionally, state privacy laws such as the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (CDPA) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) provide consumers with the right to access, delete, and opt-out of the sale of their personal information.
Global Impact of Data Privacy Laws
Geolocation data privacy laws have a global impact as they affect how companies collect and use personal information across borders. For example, the GDPR applies to any company that collects and processes personal data of EU citizens, regardless of where the company is located. This means that companies outside the EU must comply with the GDPR if they collect and process the personal data of EU citizens. Similarly, the CPRA applies to any company that collects and processes the personal data of California residents, regardless of where the company is located.
Consent and Control in Data Sharing
Geolocation data privacy laws are essential to protect individuals’ privacy rights in the digital age. One of the key principles of these laws is the requirement for express consent from individuals before their location data can be collected and processed. This section will explore the importance of consent and control in data sharing, including the necessity of express consent, managing consent for location services, and restrictions on data controllers.
The Necessity of Express Consent
Express consent is a fundamental aspect of geolocation data privacy laws. It requires individuals to provide explicit permission for their location data to be collected, stored, and processed. This means that data controllers must inform individuals about the purposes for which their location data will be used, and obtain their explicit consent before collecting any data.
Express consent ensures that individuals have control over their location data and can make informed decisions about how it is used. It also helps to prevent the collection of location data without individuals’ knowledge or consent, which can be a serious violation of their privacy rights.
Managing Consent for Location Services
Managing consent for location services can be challenging, as individuals may not always be aware of the types of location data that are being collected. This is particularly true for mobile apps, which may collect location data even when they are not in use.
To address this issue, geolocation data privacy laws require data controllers to provide clear and concise information about the types of location data that are being collected and how they will be used. This information must be presented in a way that is easy for individuals to understand, and must be provided in advance of any data collection.
Restrictions on Data Controllers
Geolocation data privacy laws also place restrictions on data controllers, limiting the ways in which they can collect, store, and process location data. For example, data controllers may be required to implement technical and organizational measures to protect location data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
Data controllers may also be required to delete location data once it is no longer necessary for the purposes for which it was collected. These restrictions help to ensure that individuals have control over their location data and that it is not used in ways that could harm their privacy rights.
Challenges and Enforcement
Privacy Risks and Concerns
Geolocation data privacy laws have become essential due to the increasing privacy concerns and risks associated with the use of geolocation data. The collection and processing of geolocation data can reveal sensitive information about individuals, including their daily routines, habits, and whereabouts. This information can be used to track individuals, monitor their behavior, and potentially invade their privacy. Legislators and privacy advocates have raised concerns about the potential misuse of geolocation data by companies and other entities. They argue that the lack of clear rules and regulations governing the collection and processing of geolocation data has created a privacy gap that needs to be addressed.
Legislation and Enforcement Issues
The enforcement of geolocation data privacy laws has been a challenge for many jurisdictions. Lawsuits and enforcement issues have arisen in states like Virginia, where enforcement authorities have struggled to enforce geolocation data privacy laws due to the lack of clear rules and regulations. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has been at the forefront of the privacy shift, calling for stronger privacy laws and regulations to protect consumers’ privacy. The FTC has also issued guidelines for companies and other entities on how to collect and process geolocation data in a privacy-compliant manner.
Frequently Asked Questions
What implications does GDPR have on the management of geolocation data?
GDPR requires consent for geolocation data and fines for non-compliance.
How does the CCPA define geolocation data and its protection?
CCPA defines and protects geolocation data with notice and consent.
In what ways can individuals exercise control over their geolocation data?
Users control geolocation data through device settings and opt-outs.
What are the potential risks of not protecting geolocation data under laws like the CPRA?
Risks include identity theft and harm from misuse of geolocation data.
How does the Geolocation Privacy and Surveillance Act impact data privacy?
The GPS Act mandates warrants for law enforcement to access geolocation data.
Why is it crucial to understand the protection of location privacy in the digital age?
Understanding safeguards against misuse informs choices and protects privacy.